The amount of heat consumed by households for heating will continue to decline. The causes of this trend, we can identify more, but they all have one common feature - the growing cost of heat. It is growing because of rising prices of inputs (raw materials, technology, labor) but also due to decreasing consumption of heat (climate change, saving measures).
Archiv článků od 26.1.2015 do 16.11.2015
In the presented article is analyzed aging of the photovoltaic power plant panels located in Dukovany. Photovoltaic power plant in Dukovany (identified also as PV power plant) is the oldest PV power plants built in the Czech Republic. PV power plant was put into service in 1998. After 17 years of working is slowly ending its life. This work compared an electricity production in individual years, decreasing of produce energy from the values given by the manufacturer and also describing visible defects on selected modules.
The heating period 2014/2015 in Prague based on the observation of Prague-Karlov station was with 222 days, a little shorter, and with an average temperature of 6,4 °C, slightly warmer than the long-term average. Basic characteristic of heat demand for heating is 2803 D°(19) degree days, heat demand is much lower than the long-term average of 3227 D°(19). It's the second lowest number of degree days of the heating period since the beginning of the century.
The last time we meet with the requirement to improve energy efficiency practically every step, as a result of the implementation of Directive 2012/27/EU into our legislation. The purpose of this regulation is to cause such changes in society and in the energy sector to increase energy efficiency in 2020 by 20% and created the conditions for its further growth in the longer term. The most important area in terms of energy consumption includes heating of buildings.
The article deals with the change of the basic standard for flue gas of heating appliances. It draws attention to the illegality of technically unjustified distances between flue outlets on the facade and windows or other building openings. The specified distances lead to practical ban on installation of considerably cheaper gas boilers with the flue gas outlet through the facade.
In May 2015 Centre for Public Opinion Research (CVVM) conducted public opinion poll, whose results published on its website. Surprisingly, the environmental organization Calla that openly opposes the development of nuclear energy, interprets the results more balanced than the Czech News Agency (ČTK), which should be independent. Interpretation of ČTK is more nuclear-optimistic than the results of the poll. It is worth noting the contradiction between the answers to the first and second questions. On one hand most respondents (45 %) prefer conservation of share of nuclear energy (22 % for increase and 22 % for decrease). On other hand most respondents (44 % against 39 %) prefer to build two more nuclear units at Temelin. Building of two new units at Temelin would definitely lead to an increase in the share of nuclear energy.
Article freely continues the theme of thermodynamic analysis of phenomena occurring in and around the pipeline construction, located in the sandy backfill, now with respect to theoretical foundations, describing the related effects of heat transfer. The article includes in particular the currently known insights into heat exchange in the case where the thermally insulated pipes placed near each other in the soil backfill. Individual processes intended to evaluate size of heat loss are used in the model calculation example a specific pipeline, whose real insulating state has previously been verified by measurement.
Article freely continues the theme of thermodynamic analysis of phenomena occurring in and around the pipeline construction, located in the sandy backfill, now with respect to theoretical foundations, describing the related effects of heat transfer. The article includes in particular the currently known insights into heat exchange in the case where the thermally insulated pipes placed near each other in the soil backfill. Individual processes intended to evaluate size of heat loss are used in the model calculation example a specific pipeline, whose real insulating state has previously been verified by measurement.
In Europe, individual Member States are responsible for energy. Different countries take different approach. Complete ban on mining exists, for example, in Bulgaria, France and certain regions in Germany. On the contrary, Poland and Ukraine aim to develop shale gas mining in order to reduce their dependency on gas import from Russia. At EU level, there is currently no unified legislation covering exploration and exploitation of unconventional gas resources. Mining in EU, however, falls under the general European agreements and directives, including Treaty on the EU Water Framework Directive, Directive on the assessment of environmental impact, the Directive on waste from mining and regulatory framework for management of chemical substances REACH.
Hydraulic fracturing raises concerns regarding possible contamination of groundwater resources, adverse effects on air quality, potential leaks of gas and other substances, treatment of waste material and various direct and indirect health hazards. Water used in hydraulic fracturing contains roughly 0.5 % of chemical additives including agents for reducing friction, preventing corrosion, eliminating microorganisms, gels and lubricants used for cooling the drill head etc. Serious debate concerning potential risks of commercial shale gas mining is taking place today throughout Europe.
In 2013, electric power generated in the Czech Republic in power plants using various primary energy resources reached 87.06 TWh (gross production). The gross domestic consumption was 70.18 TWh. The diagrams presented and the annual balance clearly show that the biggest electric power producers in the Czech Republic continue to be coal-burning power plants. The usage of electricity produced from renewable resources for regulation of the production is limited by the fact that these resources (FVT, VTE, biogas power plants and small water power plants) have an unlimited priority access to the distribution network and are not regulated in any way.
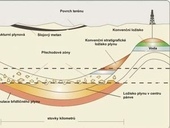
Shales are sedimentary rocks. They are typically found in horizontal formations. Shale gas extraction therefore requires that miners “bend“ the drill head when approaching the layer with shale deposits and drill horizontally. It is also necessary to create large number of small cracks in the rock which allow the gas to escape. This is achieved by pumping large amounts of water with sand and other additives under pressure into the well. This process is called hydraulic fracturing or fracking.
Total recoverable shale gas reserves in China are currently estimated at 31.5 trillion cubic meters, which amounts to second largest (after USA) shale gas reserves in the world. Other Asian shale gas resources are located in India and Pakistan, Indonesia, Australia and Russia. Deposits of shale gas with potential for mining are also found in North and South Africa, Middle East and throughout Europe.
First shale gas mining activities started in Appalachian mountains in United States of America in 1821. Since the start of 21st century shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States. The focus on unconventional gas resources gradually spreads also to other parts of the world. Shale gas reserves worldwide are estimated at 331 trillion cubic meters. The largest producer of shale gas today is USA, but plans to develop shale gas mining are considered also in other parts of the world – from Europe to South Africa, from China to Argentina.
This article is the second continuation of a series of articles on the topic of mapping thermodynamic phenomena in backfilled pipe and its surroundings. An integral part of the investigation of phenomena affecting the operation of district heating networks in particular, is the correct determination of hydraulic parameters. These are mapped to the correct operation of the piping system and the resulting economic operation. Readers now present text is the current status of researches in this field and should be information about current approaches to solving the hydraulic conditions in the heating industry.
Shale gas is natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Main source of organic matter for genesis of oil and natural gas was plankton. Gradual and lengthy process of oil formation took place in past geological periods and lasted millions of years. Movement of emerged oil and natural gas from source rock to other geologic formations is called migration. We distinguish between primary and secondary migration. The deposits of hydrocarbons are usually divided to conventional and unconventional.
PID = Potential Induced Degradation refers to the physical phenomenon that causes seemingly inexplicable reduction in output from photovoltaic panels. Basically, the interlayer polarization leading to irreversible degradation of silicon photovoltaic panels. PID typically begins to appear after 2-4 years of operation, and may cause performance degradation of the solar panel according to the type and location of the panel in the string up to 70 percent. In case of an early solution, PID is reversible. PV module can be depolarize and return them almost original performance.
zpět na aktuální články